VO2 max cycling: How to improve, training plans, & best intervals

Nov 28, 2024

VO2 max cycling: How to improve, training plans, & best intervals
Nov 28, 2024

VO2 max cycling: How to improve, training plans, & best intervals

Nov 28, 2024

Improving VO2 max is one of the most effective strategies for improving cycling performance. VO2 max is a critical metric that indicates how efficiently your body utilizes oxygen during exercise, serving as an important indicator of cardiovascular fitness.
For cyclists, a high VO2 max allows for sustained and faster speeds over longer durations, ultimately leading to greater strength and efficiency on the bike.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of VO2 max, covering everything from how to calculate it, the various factors that influence it, and the most effective training plans and interval workouts to boost it.
Improving VO2 max is one of the most effective strategies for improving cycling performance. VO2 max is a critical metric that indicates how efficiently your body utilizes oxygen during exercise, serving as an important indicator of cardiovascular fitness.
For cyclists, a high VO2 max allows for sustained and faster speeds over longer durations, ultimately leading to greater strength and efficiency on the bike.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of VO2 max, covering everything from how to calculate it, the various factors that influence it, and the most effective training plans and interval workouts to boost it.
Improving VO2 max is one of the most effective strategies for improving cycling performance. VO2 max is a critical metric that indicates how efficiently your body utilizes oxygen during exercise, serving as an important indicator of cardiovascular fitness.
For cyclists, a high VO2 max allows for sustained and faster speeds over longer durations, ultimately leading to greater strength and efficiency on the bike.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of VO2 max, covering everything from how to calculate it, the various factors that influence it, and the most effective training plans and interval workouts to boost it.

JOIN takes your cycling to the next level
Looking for a smarter way to train? JOIN creates customized cycling plans based on your goals and progress, making sure you're always on track.

JOIN takes your cycling to the next level
Looking for a smarter way to train? JOIN creates customized cycling plans based on your goals and progress, making sure you're always on track.

JOIN takes your cycling to the next level
Looking for a smarter way to train? JOIN creates customized cycling plans based on your goals and progress, making sure you're always on track.
VO2 max: a short definition
VO2 max is a key metric indicating the maximum capacity of the heart, lungs, and muscles to absorb and utilize oxygen. It is typically measured in liters per minute or milliliters per kilogram of body weight per minute for weight-bearing activities like cycling.
The term VO2max is derived from "V," representing volume, "O2," standing for oxygen, and "Max," indicating maximum. This metric reflects the highest volume of oxygen that an individual can effectively utilize within a specific timeframe. To calculate your VO2 max, take a look at our easy-to-use calculator.
Note: It's important to clarify that VO2max refers specifically to the oxygen available for energy production in the muscles, not merely the maximum amount of oxygen that can be inhaled or transported by the body.
While VO2 max provides valuable insight into cycling performance, it represents just one aspect of a cyclist's abilities. The measure focuses exclusively on oxygen uptake and utilization, overlooking other critical factors such as:
Muscle strength
Endurance
Technique
Strategy, and
Mental resilience.
For cyclists, VO2 max is an essential indicator of physiological capacity; however, it should not be viewed as the only determinant of success in cycling. There are instances of cyclists with exceptionally high VO2max values who did not achieve top performance levels, highlighting that cycling success involves a complex relationship between physiological and psychological traits.
Factors that increase your VO2 Max
VO2 max is a critical metric in cycling performance, along with other factors such as how efficiently your body utilizes energy and the accumulation of lactic acid in your muscles.
Improving your VO2 max should be a primary goal if you’re training seriously for cycling, as it plays a significant role in your overall performance. In this section, we'll break down the components of VO2 max, examine the factors that influence it, and discuss the types of training necessary to enhance it.
Central and Peripheral Components of VO2 max
The oxygen transport system in our bodies can be divided into two main parts: "central" factors and "peripheral" factors. Both of these play a crucial role in how well a cyclist can use oxygen during physical activity, and if they aren't functioning optimally, it can limit performance.
Central factors: Refers to the process of getting oxygen from the lungs into the bloodstream and then transporting that oxygen-rich blood to the muscles through the heart.
Peripheral factors: Deals with how oxygen moves into the muscles and how well the muscles can use it. This involves tiny blood vessels that supply the muscle fibers and the mitochondria, which are like little power plants inside the muscle cells that produce energy using oxygen.
Note: There's an ongoing debate about which factor is more important for improving an athlete's VO2 max and overall performance.
Central factors in maximum oxygen uptake
The process of getting oxygen into our bodies starts when we breathe in air, allowing oxygen to enter our lungs. From there, it moves into our bloodstream, where it gets carried to our muscles to help produce energy. This transfer of oxygen from the lungs to the blood is called "pulmonary diffusion," and it's an integral part of how our body uses oxygen during exercise.
Once the oxygen is in our blood, our heart pumps it to the muscles. This pumping action is known as "cardiac output," which refers to how much blood the heart sends out in a minute.
Cardiac output depends on two main factors:
The amount of blood the heart pumps with each beat (stroke volume) and
How fast the heart beats (heart rate).
For example, when someone starts training, improvements in stroke volume are often the biggest reason for better fitness levels. This means their heart gets better at sending more blood to their muscles. On the other hand, the way oxygen moves from the lungs to the blood and the maximum speed of the heart doesn't change much with training.
As cyclists become more experienced and their stroke volume approaches its highest level, research shows that the effectiveness of muscles at using oxygen becomes crucial for further improvements in fitness.
Peripheral factors in maximum oxygen uptake
Number of capillaries: The factors that influence an athlete's VO2 max, or maximum oxygen uptake, include the number of tiny blood vessels (capillaries) and the amount and efficiency of energy-producing structures (mitochondria) in their muscles.
The good news is that both the number of capillaries and mitochondria can be improved through effective training routines.
For example, when a cyclist trains, more capillaries develop around their muscle fibers, creating a larger area for oxygen to move from the blood into the muscles and allowing blood to flow more slowly through these vessels. This "slow flow" gives oxygen more time to be absorbed.
Efficiency of mitochondria: With more mitochondria in the muscles and increased efficiency in their function, more of the oxygen that reaches them can be used to create energy for physical activities. Additionally, having more mitochondria means that the job of using oxygen can be spread out among them, making the process more efficient.
In simple terms, the more oxygen that gets to these mitochondria, the more energy (in the form of ATP) can be produced to fuel the muscles during cycling. Since each mitochondrion can process far more oxygen than what the heart can pump out at once, the key is to ensure that as much oxygen as possible reaches them.
Gender
Women typically have a lower VO2 max than men due to physiological differences. One key aspect is heart size; men generally have larger hearts, leading to a greater stroke volume and improved blood oxygen delivery to muscles.
Additionally, the muscle fiber composition in men’s hearts often promotes better pumping efficiency. Lung capacity is also significant, as men usually have larger lung volumes, which allows for greater oxygen intake during strenuous activities.
In short, heart size, pumping capability, muscle fiber composition, and lung capacity all contribute to the higher VO2 max in men compared to women, highlighting the physiological differences that affect athletic performance.
Genetics
Individual differences in how our bodies use energy can vary from person to person, mainly depending on the type of tissue. A key part of our health is how well our cells work, which is largely influenced by tiny structures inside them called mitochondria. Exercise is known to enhance the function and number of these mitochondria.
Some inherited genes have been linked to athletic ability, especially in highly trained athletes, and also how regular people respond to exercise. However, research results haven't always been consistent.
In one study, researchers looked at a group of 62 participants who completed four weeks of a high-intensity interval training (HIIT) program. They measured key physical traits to see how much improvement occurred during the program.
Specifically, researchers looked at:
Maximum power output
Power at the point where lactic acid starts to build up in the blood
Maximum oxygen consumption
Time taken to complete a 20 km race
The findings suggested that certain genes may play a role in how well individuals respond to exercise. The researchers recommended that future studies should include a wider variety of people from different backgrounds to confirm these results.
The average VO2 max for a cyclist
The average VO2 max for cyclists typically ranges from 50 to 80 ml/kg/min for beginners, while pro cyclists may reach values as high as 90 ml/kg/min. Several factors influence VO2 max, including age, gender, genetics, and the level of physical training. Research indicates that VO2 max generally declines with age.
Because of the complex interplay between these variables, providing precise VO2 max values that apply universally can be challenging.
To help you better understand, we have compiled baseline figures that can serve as reference points for evaluating what forms an impressive VO2 max.
Average VO2 max by age
A study published in the National Library of Medicine found that highly trained athletes, averaging 62 years old, experienced a slower decline in VO2 max and maintained a steadier heart rate compared to inactive peers. Active participants saw a 5.5% VO2 max drop per decade, while inactive participants saw a 12% drop.
The athletes had been training for over 10 years before the study and continued to stay active throughout the follow-up period. For the less active group, their oxygen intake ability dropped by about 3.3 milliliters per kilogram per minute, which is around a 12% decrease every decade. Along with this, their maximum heart rate decreased by 8 beats per minute, and the amount of oxygen they used with each heartbeat also fell.
In contrast, the master athletes experienced only a 2.2 milliliters per kilogram per minute drop in their VO2 max, which translates to a 5.5% decrease each decade. Interestingly, their maximum heart rate remained steady, while their oxygen use per heartbeat slightly decreased.
These findings suggest that older athletes who regularly engage in vigorous exercise experience a slower decline in their oxygen intake capacity compared to their less active peers. Additionally, staying active may help slow the decline in heart rate that typically happens as people age.
VO2 max for professional and Tour de France cyclists
VO2 max is a measure of how effectively your body uses oxygen during exercise. It can vary based on factors such as age, gender, sports experience, and overall fitness levels.
For male cyclists, the average VO2max typically ranges from 50 to 80 ml/kg/min.
Elite cyclists often have higher values, usually between 70 and 85 ml/kg/min, and
Exceptional athletes can exceed 90 ml/kg/min.
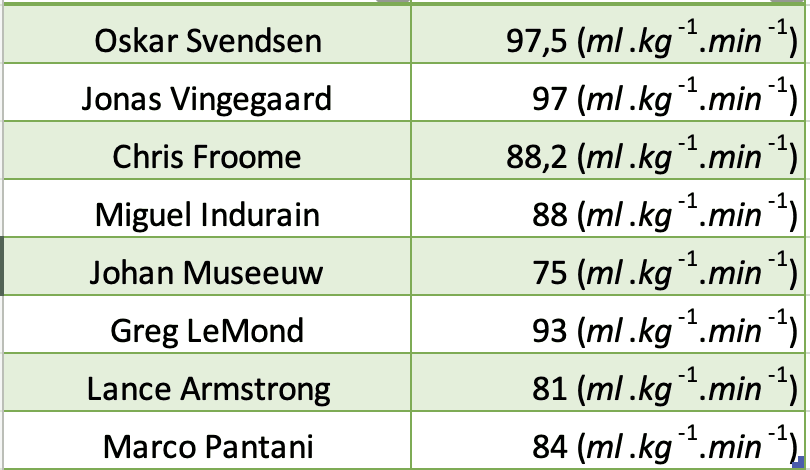
Top cyclists on the world tour and Tour de France, like Jonas Vingeragaard, reportedly have a VO2 Max of 97 ml/kg/min.
It’s important to note that these phenomenal scores might not always be reflected in scientific papers. Sometimes, the feats of very high-performing athletes are not well represented in research, leading to the impression that fewer people reach these impressive levels.
How to improve your VO2 max
Improving VO2 max involves a varied approach that goes beyond engaging in high-intensity workouts. It's important to include sustained, moderate-intensity sessions as they play a critical role in improving VO2 max. This strategy targets cardiovascular adaptations rather than focusing on muscular endurance and strength.
Interval length and VO2 max
Research by Seiler et al. emphasized the effectiveness of a specific interval training method of performing intervals structured as 4 × 8 minutes at 90% of an athlete's maximum heart rate.
This method has been shown to produce greater improvements in VO2 max compared to other interval training approaches, such as 4 × 4 minutes at a higher intensity of 95% of maximum heart rate.
The findings suggest that spending longer periods at around 90% of one's VO2 max or heart rate maximum is especially beneficial for maximizing aerobic capacity and boosting overall performance.
Surges during HIIT
Additionally, research by Rønnestad has introduced another effective strategy involving incorporating surges during high-intensity interval training (HIIT). These surges help cyclists maintain elevated VO2 max levels throughout their workouts. This adaptation can be attributed to the increased demand for oxygen occurring from changes in breathing patterns during these surges.
Note: This method does not lead to an increase in lactate levels, perceived exertion, or overall training load, making it a highly efficient strategy for improving cardiovascular performance without putting excessive stress on the body.
Building a VO2 max training plan
Designing a cycling plan to improve your VO2 max involves planning structured workouts that specifically target improvements in aerobic capacity. As we've seen, VO2 max is an important metric of your body's ability to utilize oxygen during exercise, and increasing this metric can greatly enhance your endurance and overall performance.
1. Establish your baseline
To get started, consider undergoing a professional VO2 max test. Alternatively, you can use estimated values from various fitness devices or take one of our free FTP tests to gain insights into your aerobic capacity. If you have access to a power meter, it's a good idea to determine your functional threshold power (FTP). Your FTP indicates the highest power output you can sustain for roughly an hour and serves as a vital metric for setting the intensity of your training sessions.
2. Define training zones
To effectively define your training zones, consider utilizing your Functional Threshold Power (FTP) or heart rate metrics. Of particular importance is your VO2 max zone, which is generally characterized by intensities ranging from:
90% to 105% of your FTP or
95% to 100% of your maximum heart rate.
Pushing into the higher VO2 max zone is where you should concentrate your efforts to enhance your VO2 max capacity. This zone is best approached through interval training, allowing you to maximize your performance gains.
3. Plan complementing workouts
Engaging in long, steady rides at a low intensity is important for developing your aerobic base. This foundation is vital for improving your VO2 max, which ultimately supports better endurance. Additionally, incorporating sessions at or near your FTP can significantly boost your ability to maintain a high pace.
4. Consider frequency and progression
It's a good idea to start with one or two intense workouts focused on improving your VO2 max each week. To allow your body to recover properly, try not to have more than two of these hard sessions a week. As you get fitter, you can gradually increase the number or length of these intervals.
VO2 max intervals
As stated above, you can improve your VO2 max through training, which was previously thought to be relatively fixed. This makes sense, as our bodies are quite capable of becoming more efficient at using oxygen when we engage in regular workouts.
Research shows that you can enhance your VO2 max not only through challenging, high-intensity workouts but also by engaging in longer, easier rides. A combination of both, namely interval training, typically delivers the best results.
Note: While most people can improve their aerobic fitness, the level of improvement can differ greatly based on genetics. So, some may see more significant gains than others.
Workouts to increase your VO2 max
Below are four of our highly recommended VO2 max workouts specifically designed to improve your top-end cycling performance.
1. 30-15’s Ronnestad Intervals
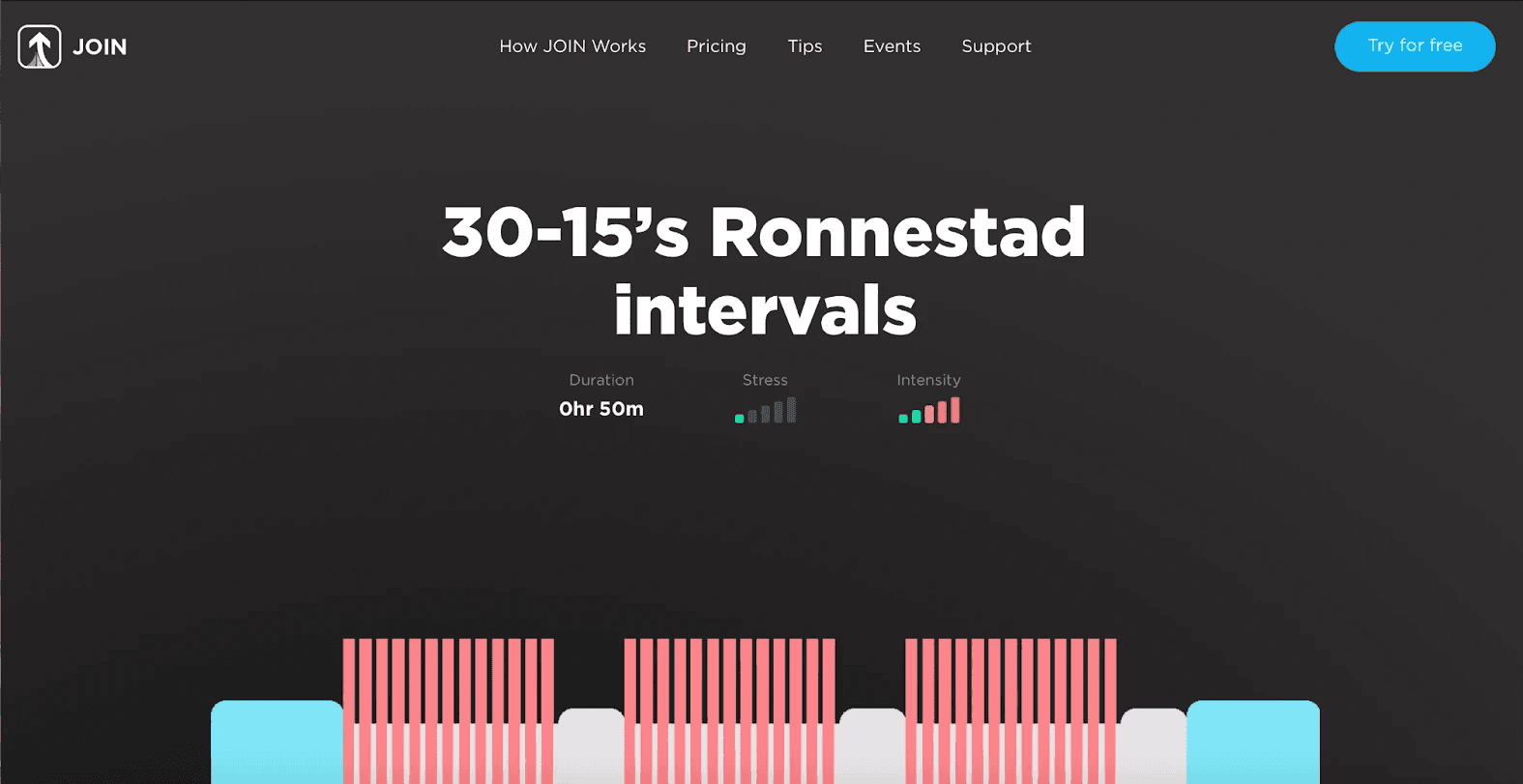
Perform 3 sets of 13 reps with intervals of 30 seconds of effort followed by 15 seconds of rest. Aim for an intensity that is challenging yet sustainable throughout all intervals. During the 30-second work phase, focus on increasing your speed, particularly in the first 10 seconds. Use the 15-second rest intervals to let your legs recover and fall back into a relaxed position.
This workout is great for getting you accustomed to the intensity and rigor of what it feels like to target your upper levels of aerobic fitness and improve your VO2 max. The workout itself is under 1 hour, making it ideal for the time-crunched rider.
2. 2 Sets 3 x 3 minute VO2max

Complete 2 sets of intervals, each lasting 3 minutes, aimed at maximizing your VO2max. During these intervals, exert your maximum effort while keeping the intensity consistent throughout. Focus on evenly distributing your effort, maintaining the same intensity level across all intervals within each set.
At 2 hours in length, this workout is perfect for the slightly more advanced rider looking to get a good amount of foundational intensity in, along with training sets to boost your VO2 max.
Try this advanced interval cycling workout for free on JOIN.
3. All In One
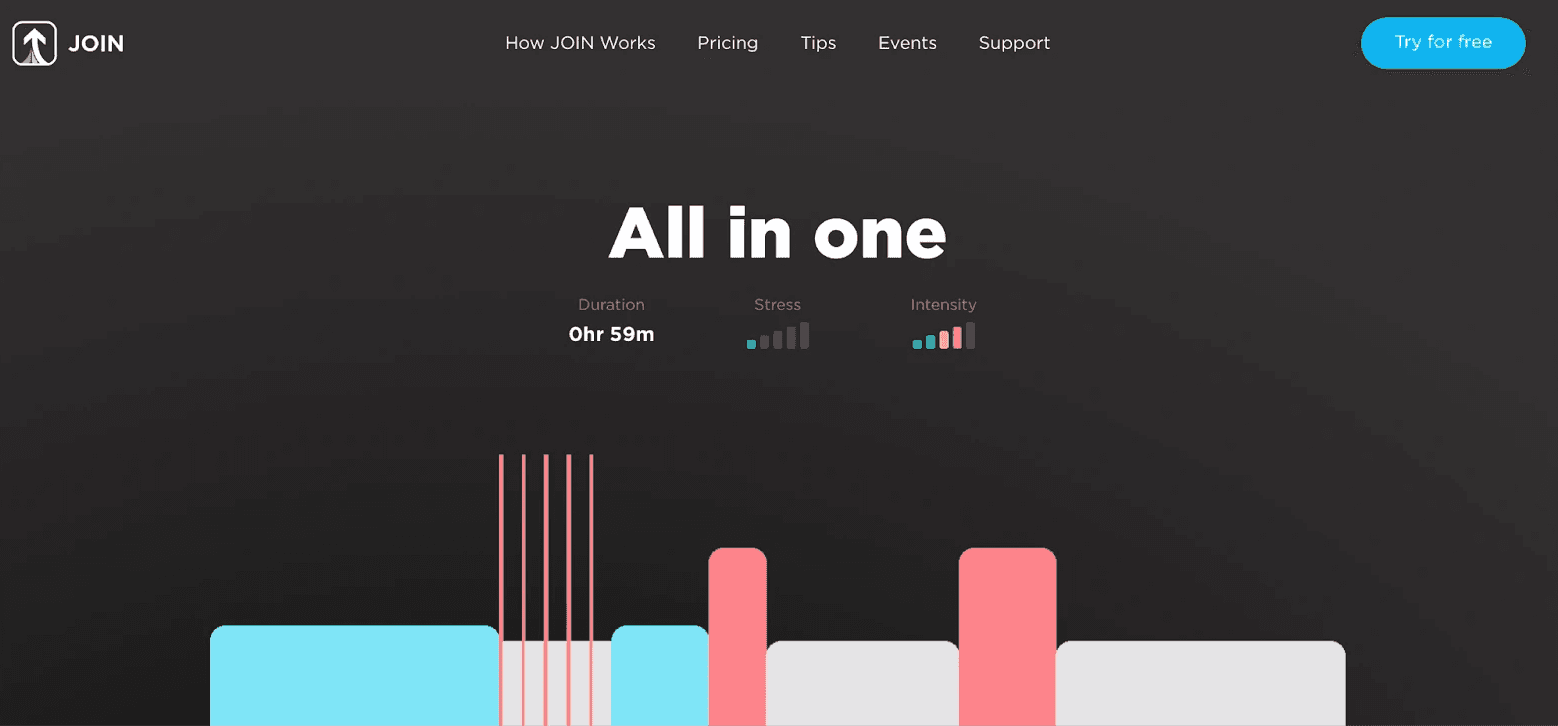
Begin your workout with 3 intense 10-second sprints, pushing yourself to the absolute limit with each burst of speed. After this initial challenge, take 1-minute to catch your breath and let your heart rate recover. Next, dive into a demanding 2-minute VO2 max interval, where you'll aim to sustain high intensity and maximize your oxygen consumption.
Following this effort, allow yourself a 3-minute rest to regroup and prepare for the final push. When you're ready, unleash all your energy in a grueling 5-minute all-out effort, giving it everything you've got until the very end.
This workout plan is perfect for those riders looking to take their VO2 max to the next level. With a combination of intensities and durations, you’ll be kept on your toes and need to stay alert. If you struggle to push hard toward the end of rides, this workout is for you.
Try the 'All in one' cycling workout for free.
4. Breakaway Bingo
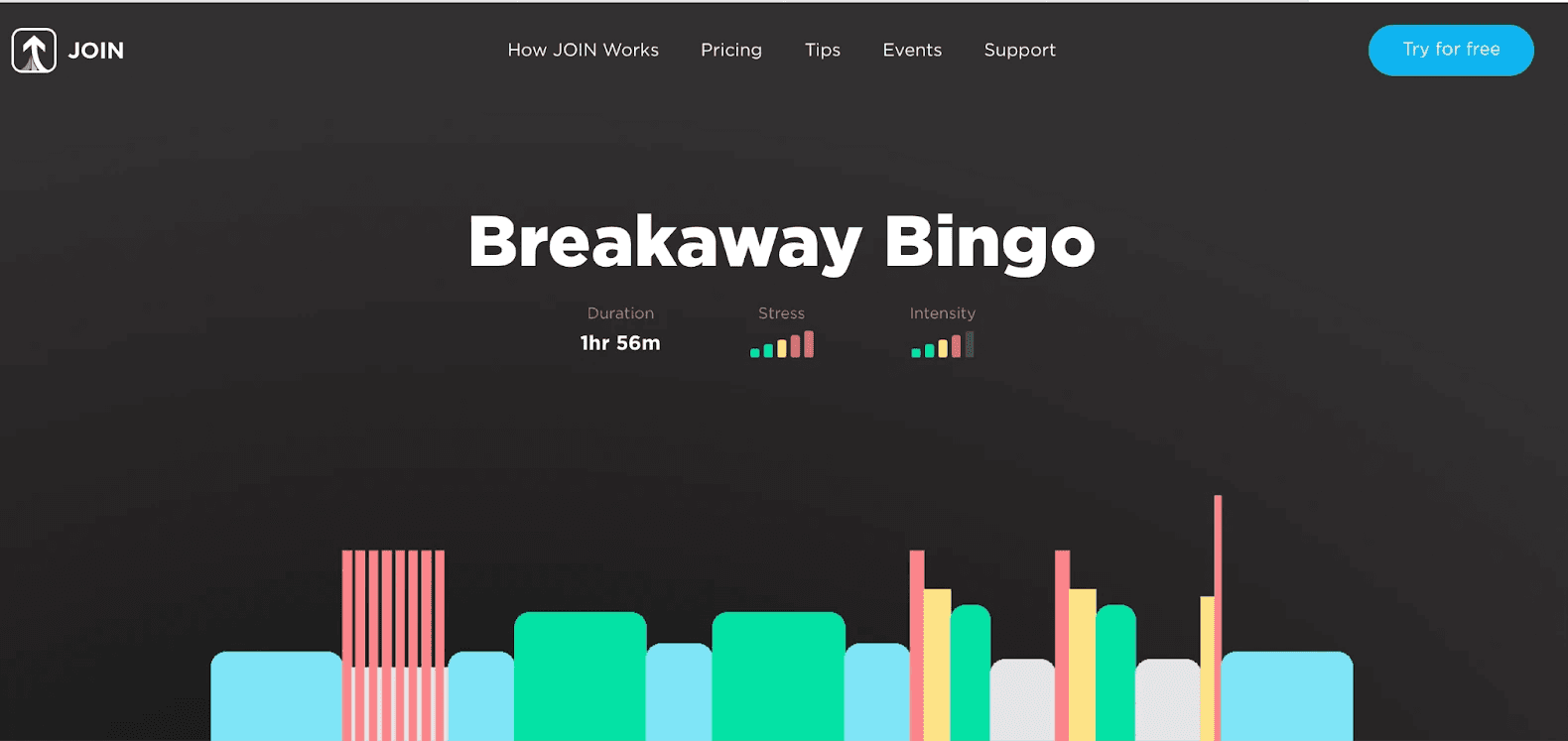
One of our personal favorites, Breakaway Bingo is a highly effective VO2 max workout that can simulate the dynamics of an entire race in one session. This workout includes various phases, such as practicing getting in the breakaway, performing steady head turns, executing accelerations, and topping it all off in a final sprint to secure victory. This structured yet fun and challenging plan enhances both endurance and racing strategies.
Test your racing endurance with JOIN's 'Breakaway Bingo' workout.
The VO2 max training plan that adjusts to your schedule
If you’re confused and having trouble finding a plan that improves your VO2 max, try JOIN.
JOIN offers a flexible approach to incorporating workouts into your busy schedule. Your program adapts to your fitness level and availability in real-time, ensuring that each session is tailored to be both challenging and manageable.
Try JOIN for free and take your VO2 Max to new heights.
VO2 max: a short definition
VO2 max is a key metric indicating the maximum capacity of the heart, lungs, and muscles to absorb and utilize oxygen. It is typically measured in liters per minute or milliliters per kilogram of body weight per minute for weight-bearing activities like cycling.
The term VO2max is derived from "V," representing volume, "O2," standing for oxygen, and "Max," indicating maximum. This metric reflects the highest volume of oxygen that an individual can effectively utilize within a specific timeframe. To calculate your VO2 max, take a look at our easy-to-use calculator.
Note: It's important to clarify that VO2max refers specifically to the oxygen available for energy production in the muscles, not merely the maximum amount of oxygen that can be inhaled or transported by the body.
While VO2 max provides valuable insight into cycling performance, it represents just one aspect of a cyclist's abilities. The measure focuses exclusively on oxygen uptake and utilization, overlooking other critical factors such as:
Muscle strength
Endurance
Technique
Strategy, and
Mental resilience.
For cyclists, VO2 max is an essential indicator of physiological capacity; however, it should not be viewed as the only determinant of success in cycling. There are instances of cyclists with exceptionally high VO2max values who did not achieve top performance levels, highlighting that cycling success involves a complex relationship between physiological and psychological traits.
Factors that increase your VO2 Max
VO2 max is a critical metric in cycling performance, along with other factors such as how efficiently your body utilizes energy and the accumulation of lactic acid in your muscles.
Improving your VO2 max should be a primary goal if you’re training seriously for cycling, as it plays a significant role in your overall performance. In this section, we'll break down the components of VO2 max, examine the factors that influence it, and discuss the types of training necessary to enhance it.
Central and Peripheral Components of VO2 max
The oxygen transport system in our bodies can be divided into two main parts: "central" factors and "peripheral" factors. Both of these play a crucial role in how well a cyclist can use oxygen during physical activity, and if they aren't functioning optimally, it can limit performance.
Central factors: Refers to the process of getting oxygen from the lungs into the bloodstream and then transporting that oxygen-rich blood to the muscles through the heart.
Peripheral factors: Deals with how oxygen moves into the muscles and how well the muscles can use it. This involves tiny blood vessels that supply the muscle fibers and the mitochondria, which are like little power plants inside the muscle cells that produce energy using oxygen.
Note: There's an ongoing debate about which factor is more important for improving an athlete's VO2 max and overall performance.
Central factors in maximum oxygen uptake
The process of getting oxygen into our bodies starts when we breathe in air, allowing oxygen to enter our lungs. From there, it moves into our bloodstream, where it gets carried to our muscles to help produce energy. This transfer of oxygen from the lungs to the blood is called "pulmonary diffusion," and it's an integral part of how our body uses oxygen during exercise.
Once the oxygen is in our blood, our heart pumps it to the muscles. This pumping action is known as "cardiac output," which refers to how much blood the heart sends out in a minute.
Cardiac output depends on two main factors:
The amount of blood the heart pumps with each beat (stroke volume) and
How fast the heart beats (heart rate).
For example, when someone starts training, improvements in stroke volume are often the biggest reason for better fitness levels. This means their heart gets better at sending more blood to their muscles. On the other hand, the way oxygen moves from the lungs to the blood and the maximum speed of the heart doesn't change much with training.
As cyclists become more experienced and their stroke volume approaches its highest level, research shows that the effectiveness of muscles at using oxygen becomes crucial for further improvements in fitness.
Peripheral factors in maximum oxygen uptake
Number of capillaries: The factors that influence an athlete's VO2 max, or maximum oxygen uptake, include the number of tiny blood vessels (capillaries) and the amount and efficiency of energy-producing structures (mitochondria) in their muscles.
The good news is that both the number of capillaries and mitochondria can be improved through effective training routines.
For example, when a cyclist trains, more capillaries develop around their muscle fibers, creating a larger area for oxygen to move from the blood into the muscles and allowing blood to flow more slowly through these vessels. This "slow flow" gives oxygen more time to be absorbed.
Efficiency of mitochondria: With more mitochondria in the muscles and increased efficiency in their function, more of the oxygen that reaches them can be used to create energy for physical activities. Additionally, having more mitochondria means that the job of using oxygen can be spread out among them, making the process more efficient.
In simple terms, the more oxygen that gets to these mitochondria, the more energy (in the form of ATP) can be produced to fuel the muscles during cycling. Since each mitochondrion can process far more oxygen than what the heart can pump out at once, the key is to ensure that as much oxygen as possible reaches them.
Gender
Women typically have a lower VO2 max than men due to physiological differences. One key aspect is heart size; men generally have larger hearts, leading to a greater stroke volume and improved blood oxygen delivery to muscles.
Additionally, the muscle fiber composition in men’s hearts often promotes better pumping efficiency. Lung capacity is also significant, as men usually have larger lung volumes, which allows for greater oxygen intake during strenuous activities.
In short, heart size, pumping capability, muscle fiber composition, and lung capacity all contribute to the higher VO2 max in men compared to women, highlighting the physiological differences that affect athletic performance.
Genetics
Individual differences in how our bodies use energy can vary from person to person, mainly depending on the type of tissue. A key part of our health is how well our cells work, which is largely influenced by tiny structures inside them called mitochondria. Exercise is known to enhance the function and number of these mitochondria.
Some inherited genes have been linked to athletic ability, especially in highly trained athletes, and also how regular people respond to exercise. However, research results haven't always been consistent.
In one study, researchers looked at a group of 62 participants who completed four weeks of a high-intensity interval training (HIIT) program. They measured key physical traits to see how much improvement occurred during the program.
Specifically, researchers looked at:
Maximum power output
Power at the point where lactic acid starts to build up in the blood
Maximum oxygen consumption
Time taken to complete a 20 km race
The findings suggested that certain genes may play a role in how well individuals respond to exercise. The researchers recommended that future studies should include a wider variety of people from different backgrounds to confirm these results.
The average VO2 max for a cyclist
The average VO2 max for cyclists typically ranges from 50 to 80 ml/kg/min for beginners, while pro cyclists may reach values as high as 90 ml/kg/min. Several factors influence VO2 max, including age, gender, genetics, and the level of physical training. Research indicates that VO2 max generally declines with age.
Because of the complex interplay between these variables, providing precise VO2 max values that apply universally can be challenging.
To help you better understand, we have compiled baseline figures that can serve as reference points for evaluating what forms an impressive VO2 max.
Average VO2 max by age
A study published in the National Library of Medicine found that highly trained athletes, averaging 62 years old, experienced a slower decline in VO2 max and maintained a steadier heart rate compared to inactive peers. Active participants saw a 5.5% VO2 max drop per decade, while inactive participants saw a 12% drop.
The athletes had been training for over 10 years before the study and continued to stay active throughout the follow-up period. For the less active group, their oxygen intake ability dropped by about 3.3 milliliters per kilogram per minute, which is around a 12% decrease every decade. Along with this, their maximum heart rate decreased by 8 beats per minute, and the amount of oxygen they used with each heartbeat also fell.
In contrast, the master athletes experienced only a 2.2 milliliters per kilogram per minute drop in their VO2 max, which translates to a 5.5% decrease each decade. Interestingly, their maximum heart rate remained steady, while their oxygen use per heartbeat slightly decreased.
These findings suggest that older athletes who regularly engage in vigorous exercise experience a slower decline in their oxygen intake capacity compared to their less active peers. Additionally, staying active may help slow the decline in heart rate that typically happens as people age.
VO2 max for professional and Tour de France cyclists
VO2 max is a measure of how effectively your body uses oxygen during exercise. It can vary based on factors such as age, gender, sports experience, and overall fitness levels.
For male cyclists, the average VO2max typically ranges from 50 to 80 ml/kg/min.
Elite cyclists often have higher values, usually between 70 and 85 ml/kg/min, and
Exceptional athletes can exceed 90 ml/kg/min.
Top cyclists on the world tour and Tour de France, like Jonas Vingeragaard, reportedly have a VO2 Max of 97 ml/kg/min.
It’s important to note that these phenomenal scores might not always be reflected in scientific papers. Sometimes, the feats of very high-performing athletes are not well represented in research, leading to the impression that fewer people reach these impressive levels.

How to improve your VO2 max
Improving VO2 max involves a varied approach that goes beyond engaging in high-intensity workouts. It's important to include sustained, moderate-intensity sessions as they play a critical role in improving VO2 max. This strategy targets cardiovascular adaptations rather than focusing on muscular endurance and strength.
Interval length and VO2 max
Research by Seiler et al. emphasized the effectiveness of a specific interval training method of performing intervals structured as 4 × 8 minutes at 90% of an athlete's maximum heart rate.
This method has been shown to produce greater improvements in VO2 max compared to other interval training approaches, such as 4 × 4 minutes at a higher intensity of 95% of maximum heart rate.
The findings suggest that spending longer periods at around 90% of one's VO2 max or heart rate maximum is especially beneficial for maximizing aerobic capacity and boosting overall performance.
Surges during HIIT
Additionally, research by Rønnestad has introduced another effective strategy involving incorporating surges during high-intensity interval training (HIIT). These surges help cyclists maintain elevated VO2 max levels throughout their workouts. This adaptation can be attributed to the increased demand for oxygen occurring from changes in breathing patterns during these surges.
Note: This method does not lead to an increase in lactate levels, perceived exertion, or overall training load, making it a highly efficient strategy for improving cardiovascular performance without putting excessive stress on the body.
Building a VO2 max training plan
Designing a cycling plan to improve your VO2 max involves planning structured workouts that specifically target improvements in aerobic capacity. As we've seen, VO2 max is an important metric of your body's ability to utilize oxygen during exercise, and increasing this metric can greatly enhance your endurance and overall performance.
1. Establish your baseline
To get started, consider undergoing a professional VO2 max test. Alternatively, you can use estimated values from various fitness devices or take one of our free FTP tests to gain insights into your aerobic capacity. If you have access to a power meter, it's a good idea to determine your functional threshold power (FTP). Your FTP indicates the highest power output you can sustain for roughly an hour and serves as a vital metric for setting the intensity of your training sessions.
2. Define training zones
To effectively define your training zones, consider utilizing your Functional Threshold Power (FTP) or heart rate metrics. Of particular importance is your VO2 max zone, which is generally characterized by intensities ranging from:
90% to 105% of your FTP or
95% to 100% of your maximum heart rate.
Pushing into the higher VO2 max zone is where you should concentrate your efforts to enhance your VO2 max capacity. This zone is best approached through interval training, allowing you to maximize your performance gains.
3. Plan complementing workouts
Engaging in long, steady rides at a low intensity is important for developing your aerobic base. This foundation is vital for improving your VO2 max, which ultimately supports better endurance. Additionally, incorporating sessions at or near your FTP can significantly boost your ability to maintain a high pace.
4. Consider frequency and progression
It's a good idea to start with one or two intense workouts focused on improving your VO2 max each week. To allow your body to recover properly, try not to have more than two of these hard sessions a week. As you get fitter, you can gradually increase the number or length of these intervals.
VO2 max intervals
As stated above, you can improve your VO2 max through training, which was previously thought to be relatively fixed. This makes sense, as our bodies are quite capable of becoming more efficient at using oxygen when we engage in regular workouts.
Research shows that you can enhance your VO2 max not only through challenging, high-intensity workouts but also by engaging in longer, easier rides. A combination of both, namely interval training, typically delivers the best results.
Note: While most people can improve their aerobic fitness, the level of improvement can differ greatly based on genetics. So, some may see more significant gains than others.
Workouts to increase your VO2 max
Below are four of our highly recommended VO2 max workouts specifically designed to improve your top-end cycling performance.
1. 30-15’s Ronnestad Intervals

Perform 3 sets of 13 reps with intervals of 30 seconds of effort followed by 15 seconds of rest. Aim for an intensity that is challenging yet sustainable throughout all intervals. During the 30-second work phase, focus on increasing your speed, particularly in the first 10 seconds. Use the 15-second rest intervals to let your legs recover and fall back into a relaxed position.
This workout is great for getting you accustomed to the intensity and rigor of what it feels like to target your upper levels of aerobic fitness and improve your VO2 max. The workout itself is under 1 hour, making it ideal for the time-crunched rider.
2. 2 Sets 3 x 3 minute VO2max

Complete 2 sets of intervals, each lasting 3 minutes, aimed at maximizing your VO2max. During these intervals, exert your maximum effort while keeping the intensity consistent throughout. Focus on evenly distributing your effort, maintaining the same intensity level across all intervals within each set.
At 2 hours in length, this workout is perfect for the slightly more advanced rider looking to get a good amount of foundational intensity in, along with training sets to boost your VO2 max.
Try this advanced interval cycling workout for free on JOIN.
3. All In One

Begin your workout with 3 intense 10-second sprints, pushing yourself to the absolute limit with each burst of speed. After this initial challenge, take 1-minute to catch your breath and let your heart rate recover. Next, dive into a demanding 2-minute VO2 max interval, where you'll aim to sustain high intensity and maximize your oxygen consumption.
Following this effort, allow yourself a 3-minute rest to regroup and prepare for the final push. When you're ready, unleash all your energy in a grueling 5-minute all-out effort, giving it everything you've got until the very end.
This workout plan is perfect for those riders looking to take their VO2 max to the next level. With a combination of intensities and durations, you’ll be kept on your toes and need to stay alert. If you struggle to push hard toward the end of rides, this workout is for you.
Try the 'All in one' cycling workout for free.
4. Breakaway Bingo

One of our personal favorites, Breakaway Bingo is a highly effective VO2 max workout that can simulate the dynamics of an entire race in one session. This workout includes various phases, such as practicing getting in the breakaway, performing steady head turns, executing accelerations, and topping it all off in a final sprint to secure victory. This structured yet fun and challenging plan enhances both endurance and racing strategies.
Test your racing endurance with JOIN's 'Breakaway Bingo' workout.
The VO2 max training plan that adjusts to your schedule
If you’re confused and having trouble finding a plan that improves your VO2 max, try JOIN.
JOIN offers a flexible approach to incorporating workouts into your busy schedule. Your program adapts to your fitness level and availability in real-time, ensuring that each session is tailored to be both challenging and manageable.
Try JOIN for free and take your VO2 Max to new heights.
VO2 max: a short definition
VO2 max is a key metric indicating the maximum capacity of the heart, lungs, and muscles to absorb and utilize oxygen. It is typically measured in liters per minute or milliliters per kilogram of body weight per minute for weight-bearing activities like cycling.
The term VO2max is derived from "V," representing volume, "O2," standing for oxygen, and "Max," indicating maximum. This metric reflects the highest volume of oxygen that an individual can effectively utilize within a specific timeframe. To calculate your VO2 max, take a look at our easy-to-use calculator.
Note: It's important to clarify that VO2max refers specifically to the oxygen available for energy production in the muscles, not merely the maximum amount of oxygen that can be inhaled or transported by the body.
While VO2 max provides valuable insight into cycling performance, it represents just one aspect of a cyclist's abilities. The measure focuses exclusively on oxygen uptake and utilization, overlooking other critical factors such as:
Muscle strength
Endurance
Technique
Strategy, and
Mental resilience.
For cyclists, VO2 max is an essential indicator of physiological capacity; however, it should not be viewed as the only determinant of success in cycling. There are instances of cyclists with exceptionally high VO2max values who did not achieve top performance levels, highlighting that cycling success involves a complex relationship between physiological and psychological traits.
Factors that increase your VO2 Max
VO2 max is a critical metric in cycling performance, along with other factors such as how efficiently your body utilizes energy and the accumulation of lactic acid in your muscles.
Improving your VO2 max should be a primary goal if you’re training seriously for cycling, as it plays a significant role in your overall performance. In this section, we'll break down the components of VO2 max, examine the factors that influence it, and discuss the types of training necessary to enhance it.
Central and Peripheral Components of VO2 max
The oxygen transport system in our bodies can be divided into two main parts: "central" factors and "peripheral" factors. Both of these play a crucial role in how well a cyclist can use oxygen during physical activity, and if they aren't functioning optimally, it can limit performance.
Central factors: Refers to the process of getting oxygen from the lungs into the bloodstream and then transporting that oxygen-rich blood to the muscles through the heart.
Peripheral factors: Deals with how oxygen moves into the muscles and how well the muscles can use it. This involves tiny blood vessels that supply the muscle fibers and the mitochondria, which are like little power plants inside the muscle cells that produce energy using oxygen.
Note: There's an ongoing debate about which factor is more important for improving an athlete's VO2 max and overall performance.
Central factors in maximum oxygen uptake
The process of getting oxygen into our bodies starts when we breathe in air, allowing oxygen to enter our lungs. From there, it moves into our bloodstream, where it gets carried to our muscles to help produce energy. This transfer of oxygen from the lungs to the blood is called "pulmonary diffusion," and it's an integral part of how our body uses oxygen during exercise.
Once the oxygen is in our blood, our heart pumps it to the muscles. This pumping action is known as "cardiac output," which refers to how much blood the heart sends out in a minute.
Cardiac output depends on two main factors:
The amount of blood the heart pumps with each beat (stroke volume) and
How fast the heart beats (heart rate).
For example, when someone starts training, improvements in stroke volume are often the biggest reason for better fitness levels. This means their heart gets better at sending more blood to their muscles. On the other hand, the way oxygen moves from the lungs to the blood and the maximum speed of the heart doesn't change much with training.
As cyclists become more experienced and their stroke volume approaches its highest level, research shows that the effectiveness of muscles at using oxygen becomes crucial for further improvements in fitness.
Peripheral factors in maximum oxygen uptake
Number of capillaries: The factors that influence an athlete's VO2 max, or maximum oxygen uptake, include the number of tiny blood vessels (capillaries) and the amount and efficiency of energy-producing structures (mitochondria) in their muscles.
The good news is that both the number of capillaries and mitochondria can be improved through effective training routines.
For example, when a cyclist trains, more capillaries develop around their muscle fibers, creating a larger area for oxygen to move from the blood into the muscles and allowing blood to flow more slowly through these vessels. This "slow flow" gives oxygen more time to be absorbed.
Efficiency of mitochondria: With more mitochondria in the muscles and increased efficiency in their function, more of the oxygen that reaches them can be used to create energy for physical activities. Additionally, having more mitochondria means that the job of using oxygen can be spread out among them, making the process more efficient.
In simple terms, the more oxygen that gets to these mitochondria, the more energy (in the form of ATP) can be produced to fuel the muscles during cycling. Since each mitochondrion can process far more oxygen than what the heart can pump out at once, the key is to ensure that as much oxygen as possible reaches them.
Gender
Women typically have a lower VO2 max than men due to physiological differences. One key aspect is heart size; men generally have larger hearts, leading to a greater stroke volume and improved blood oxygen delivery to muscles.
Additionally, the muscle fiber composition in men’s hearts often promotes better pumping efficiency. Lung capacity is also significant, as men usually have larger lung volumes, which allows for greater oxygen intake during strenuous activities.
In short, heart size, pumping capability, muscle fiber composition, and lung capacity all contribute to the higher VO2 max in men compared to women, highlighting the physiological differences that affect athletic performance.
Genetics
Individual differences in how our bodies use energy can vary from person to person, mainly depending on the type of tissue. A key part of our health is how well our cells work, which is largely influenced by tiny structures inside them called mitochondria. Exercise is known to enhance the function and number of these mitochondria.
Some inherited genes have been linked to athletic ability, especially in highly trained athletes, and also how regular people respond to exercise. However, research results haven't always been consistent.
In one study, researchers looked at a group of 62 participants who completed four weeks of a high-intensity interval training (HIIT) program. They measured key physical traits to see how much improvement occurred during the program.
Specifically, researchers looked at:
Maximum power output
Power at the point where lactic acid starts to build up in the blood
Maximum oxygen consumption
Time taken to complete a 20 km race
The findings suggested that certain genes may play a role in how well individuals respond to exercise. The researchers recommended that future studies should include a wider variety of people from different backgrounds to confirm these results.
The average VO2 max for a cyclist
The average VO2 max for cyclists typically ranges from 50 to 80 ml/kg/min for beginners, while pro cyclists may reach values as high as 90 ml/kg/min. Several factors influence VO2 max, including age, gender, genetics, and the level of physical training. Research indicates that VO2 max generally declines with age.
Because of the complex interplay between these variables, providing precise VO2 max values that apply universally can be challenging.
To help you better understand, we have compiled baseline figures that can serve as reference points for evaluating what forms an impressive VO2 max.
Average VO2 max by age
A study published in the National Library of Medicine found that highly trained athletes, averaging 62 years old, experienced a slower decline in VO2 max and maintained a steadier heart rate compared to inactive peers. Active participants saw a 5.5% VO2 max drop per decade, while inactive participants saw a 12% drop.
The athletes had been training for over 10 years before the study and continued to stay active throughout the follow-up period. For the less active group, their oxygen intake ability dropped by about 3.3 milliliters per kilogram per minute, which is around a 12% decrease every decade. Along with this, their maximum heart rate decreased by 8 beats per minute, and the amount of oxygen they used with each heartbeat also fell.
In contrast, the master athletes experienced only a 2.2 milliliters per kilogram per minute drop in their VO2 max, which translates to a 5.5% decrease each decade. Interestingly, their maximum heart rate remained steady, while their oxygen use per heartbeat slightly decreased.
These findings suggest that older athletes who regularly engage in vigorous exercise experience a slower decline in their oxygen intake capacity compared to their less active peers. Additionally, staying active may help slow the decline in heart rate that typically happens as people age.
VO2 max for professional and Tour de France cyclists
VO2 max is a measure of how effectively your body uses oxygen during exercise. It can vary based on factors such as age, gender, sports experience, and overall fitness levels.
For male cyclists, the average VO2max typically ranges from 50 to 80 ml/kg/min.
Elite cyclists often have higher values, usually between 70 and 85 ml/kg/min, and
Exceptional athletes can exceed 90 ml/kg/min.
Top cyclists on the world tour and Tour de France, like Jonas Vingeragaard, reportedly have a VO2 Max of 97 ml/kg/min.
It’s important to note that these phenomenal scores might not always be reflected in scientific papers. Sometimes, the feats of very high-performing athletes are not well represented in research, leading to the impression that fewer people reach these impressive levels.

How to improve your VO2 max
Improving VO2 max involves a varied approach that goes beyond engaging in high-intensity workouts. It's important to include sustained, moderate-intensity sessions as they play a critical role in improving VO2 max. This strategy targets cardiovascular adaptations rather than focusing on muscular endurance and strength.
Interval length and VO2 max
Research by Seiler et al. emphasized the effectiveness of a specific interval training method of performing intervals structured as 4 × 8 minutes at 90% of an athlete's maximum heart rate.
This method has been shown to produce greater improvements in VO2 max compared to other interval training approaches, such as 4 × 4 minutes at a higher intensity of 95% of maximum heart rate.
The findings suggest that spending longer periods at around 90% of one's VO2 max or heart rate maximum is especially beneficial for maximizing aerobic capacity and boosting overall performance.
Surges during HIIT
Additionally, research by Rønnestad has introduced another effective strategy involving incorporating surges during high-intensity interval training (HIIT). These surges help cyclists maintain elevated VO2 max levels throughout their workouts. This adaptation can be attributed to the increased demand for oxygen occurring from changes in breathing patterns during these surges.
Note: This method does not lead to an increase in lactate levels, perceived exertion, or overall training load, making it a highly efficient strategy for improving cardiovascular performance without putting excessive stress on the body.
Building a VO2 max training plan
Designing a cycling plan to improve your VO2 max involves planning structured workouts that specifically target improvements in aerobic capacity. As we've seen, VO2 max is an important metric of your body's ability to utilize oxygen during exercise, and increasing this metric can greatly enhance your endurance and overall performance.
1. Establish your baseline
To get started, consider undergoing a professional VO2 max test. Alternatively, you can use estimated values from various fitness devices or take one of our free FTP tests to gain insights into your aerobic capacity. If you have access to a power meter, it's a good idea to determine your functional threshold power (FTP). Your FTP indicates the highest power output you can sustain for roughly an hour and serves as a vital metric for setting the intensity of your training sessions.
2. Define training zones
To effectively define your training zones, consider utilizing your Functional Threshold Power (FTP) or heart rate metrics. Of particular importance is your VO2 max zone, which is generally characterized by intensities ranging from:
90% to 105% of your FTP or
95% to 100% of your maximum heart rate.
Pushing into the higher VO2 max zone is where you should concentrate your efforts to enhance your VO2 max capacity. This zone is best approached through interval training, allowing you to maximize your performance gains.
3. Plan complementing workouts
Engaging in long, steady rides at a low intensity is important for developing your aerobic base. This foundation is vital for improving your VO2 max, which ultimately supports better endurance. Additionally, incorporating sessions at or near your FTP can significantly boost your ability to maintain a high pace.
4. Consider frequency and progression
It's a good idea to start with one or two intense workouts focused on improving your VO2 max each week. To allow your body to recover properly, try not to have more than two of these hard sessions a week. As you get fitter, you can gradually increase the number or length of these intervals.
VO2 max intervals
As stated above, you can improve your VO2 max through training, which was previously thought to be relatively fixed. This makes sense, as our bodies are quite capable of becoming more efficient at using oxygen when we engage in regular workouts.
Research shows that you can enhance your VO2 max not only through challenging, high-intensity workouts but also by engaging in longer, easier rides. A combination of both, namely interval training, typically delivers the best results.
Note: While most people can improve their aerobic fitness, the level of improvement can differ greatly based on genetics. So, some may see more significant gains than others.
Workouts to increase your VO2 max
Below are four of our highly recommended VO2 max workouts specifically designed to improve your top-end cycling performance.
1. 30-15’s Ronnestad Intervals

Perform 3 sets of 13 reps with intervals of 30 seconds of effort followed by 15 seconds of rest. Aim for an intensity that is challenging yet sustainable throughout all intervals. During the 30-second work phase, focus on increasing your speed, particularly in the first 10 seconds. Use the 15-second rest intervals to let your legs recover and fall back into a relaxed position.
This workout is great for getting you accustomed to the intensity and rigor of what it feels like to target your upper levels of aerobic fitness and improve your VO2 max. The workout itself is under 1 hour, making it ideal for the time-crunched rider.
2. 2 Sets 3 x 3 minute VO2max

Complete 2 sets of intervals, each lasting 3 minutes, aimed at maximizing your VO2max. During these intervals, exert your maximum effort while keeping the intensity consistent throughout. Focus on evenly distributing your effort, maintaining the same intensity level across all intervals within each set.
At 2 hours in length, this workout is perfect for the slightly more advanced rider looking to get a good amount of foundational intensity in, along with training sets to boost your VO2 max.
Try this advanced interval cycling workout for free on JOIN.
3. All In One

Begin your workout with 3 intense 10-second sprints, pushing yourself to the absolute limit with each burst of speed. After this initial challenge, take 1-minute to catch your breath and let your heart rate recover. Next, dive into a demanding 2-minute VO2 max interval, where you'll aim to sustain high intensity and maximize your oxygen consumption.
Following this effort, allow yourself a 3-minute rest to regroup and prepare for the final push. When you're ready, unleash all your energy in a grueling 5-minute all-out effort, giving it everything you've got until the very end.
This workout plan is perfect for those riders looking to take their VO2 max to the next level. With a combination of intensities and durations, you’ll be kept on your toes and need to stay alert. If you struggle to push hard toward the end of rides, this workout is for you.
Try the 'All in one' cycling workout for free.
4. Breakaway Bingo

One of our personal favorites, Breakaway Bingo is a highly effective VO2 max workout that can simulate the dynamics of an entire race in one session. This workout includes various phases, such as practicing getting in the breakaway, performing steady head turns, executing accelerations, and topping it all off in a final sprint to secure victory. This structured yet fun and challenging plan enhances both endurance and racing strategies.
Test your racing endurance with JOIN's 'Breakaway Bingo' workout.
The VO2 max training plan that adjusts to your schedule
If you’re confused and having trouble finding a plan that improves your VO2 max, try JOIN.
JOIN offers a flexible approach to incorporating workouts into your busy schedule. Your program adapts to your fitness level and availability in real-time, ensuring that each session is tailored to be both challenging and manageable.
Try JOIN for free and take your VO2 Max to new heights.
More Relevant Articles
Discover valuable training tips to enhance your cycling performance.
More Relevant Articles
Discover valuable training tips to enhance your cycling performance.
More Relevant Articles
Discover valuable training tips to enhance your cycling performance.

Unlock Your Cycling Potential Today
Join thousands of cyclists who have improved their performance with JOIN's training plans.

Unlock Your Cycling Potential Today
Join thousands of cyclists who have improved their performance with JOIN's training plans.
By joining, you agree to our Terms and Conditions and our Privacy Policy.

Unlock Your Cycling Potential Today
Join thousands of cyclists who have improved their performance with JOIN's training plans.
By joining, you agree to our Terms and Conditions and our Privacy Policy.



